Blog
The Arborist and Tree Care: A Comprehensive Guide to Professional Tree Management

If you look at an appealing, healthy tree, it’s easy to dismiss the fact that the tree exists as a matter of fact. But, maintaining a healthy and vibrant tree requires skill, dedication and knowledge that’s why that an arborist is required. Arborists are experts who commit themselves to ensuring that trees are cared for and in good health and also to protect the health and the safety of the people who live live within them. What exactly does an arborist’s work entails, and what impact does this have on the trees you see every day? In this article we’ll dig deep into the field of arboriculture. We’ll explore the work that an arborist performs, top ways to care for trees and how arborists can make a difference to the environment.
1. Introduction to Arborists
The trees of nature are some of the most beautiful and valuable creations. They provide shade and fresh air and also enhance the aesthetics and ecosystem of any region. For trees to be successful, they need to be taken care of and taken care of. This is where the knowledge of arborists is vital.
Arborists are professionals who have been certified and have specialization in the care and management of trees. They are knowledgeable about the nature of trees and the most effective ways to ensure their health, and also the best ways to safeguard them from disease or pests. Contrary to landscapers that are more regular, Arborists are focused on tree maintenance. They are knowledgeable and have tools to deal with a variety of issues that affect the growth of trees, their health and safety.
The job of an arborist could be neglected or overlooked their contribution for the environment is vital. Arborists are essential in ensuring that our green areas are safe and healthy. They provide essential services like the pruning process, diagnostics, plant and emergency maintenance of trees.
2. The Importance of Arborists in Tree Care
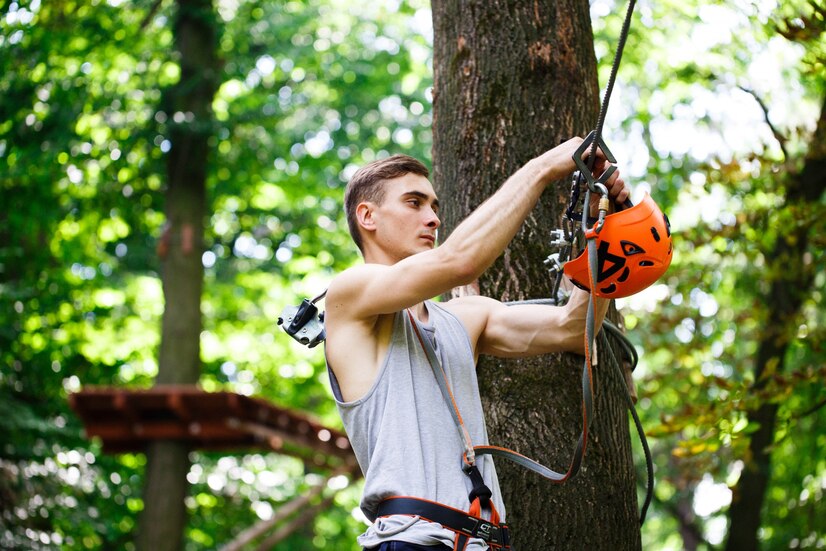

It’s likely that you’re asking why tree care is a specialization? It’s because trees are naturally growing, don’t they? The truth is that trees grow in the natural environment without interference from humans, however trees established in urban or suburban regions face a variety of problems. They are usually exposed to pollutants, pests and physical and soil compaction all of which can adversely impact their health. In addition, the trees in these areas can pose an issue for homeowners and other people if not managed properly.
Arborists are essential in identifying and addressing problems such as those, and their expertise can prevent trees from becoming unsafe or unhealthy. If they are cutting off the branches that pose danger to the tree or identifying an issue with the root, they are essential in ensuring the health and safety of the trees in every garden.
The Role of Arborists in Ecosystem Health
Beyond the care of each tree the arborists play a crucial role in the overall health of ecosystems. They shade the landscape, to reduce cities’ heat island and also contribute in the cleanness of water and air. Arborists are directly involved in this by taking care of the health of trees and maintaining the health of urban trees. They help reduce the impact of climate change by controlling trees that absorb carbon dioxide, assisting in reducing the amount of greenhouse gases that enter the atmosphere.
If there are no arborists in place, the trees may be unhealthy, unmaintained, poorly maintained, and may even pose a risk. Arborists ensure that trees are healthy and continue to build an ecologically healthy ecosystem, which will create beautiful cities and landscapes for wildlife as well as people.
3. Tree Maintenance and Care: What Arborists Do
An arborist’s primary responsibility is to look after trees, and this can involve various tasks. The most popular services for tree care are pruning trees removal, tree removal, disease control as well as pest control maintenance to make sure that trees are healthy.
Pruning and Trimming
The trimming and pruning of trees is just one of the primary services offered by arborists. The branches that have become overgrown do not only look ugly, they could also pose an hazard to safety, particularly near power lines or other structures. Pruning correctly ensures strong, healthy development and allows trees to develop in a healthy manner. Arborists can also cut trees to rid of unhealthy or dead branches that may harm the tree or result in its falling.
The timing and method of pruning are crucial. Pruning a tree that is not done incorrectly can cause damage to the growing process and even expose it to diseases and insects. Arborists are trained to understand the most efficient techniques and times to trim different types of trees.
Tree Removal
Although tree removal is typically the last resort it is sometimes the case that it is required. If a tree is suffering from condition that is structurally unstable or may pose a security threat An arborist will assess the situation and determine what is the best option. Arborists are trained to take down trees regardless of the challenging locations and adhere to all safety guidelines to prevent destruction of nearby structures or the injury of people.
Pest and Disease Control
Trees are at risk of various diseases and pests that range from fungal ailments to insect-related ailments. Arborists are skilled at diagnosing issues with the health of trees and determining the most appropriate solution for each situation. They are able to apply chemical and organic treatments if necessary to protect the tree from harmful organisms. They can also offer ways to prevent problems prior to they start.
4. Types of Arborists and Their Specializations
Although all arborists share the same knowledge of the management of trees There are different types of arborists each focused on a particular aspect in tree care.
Certified Arborists
An arborist who is certified is a person who has successfully completed the process of certification by an established professional organization like the International Society of Arboriculture (ISA). To be certified, an arborist must be able to show previous knowledge in the field, and also pass a series tests that cover topics like the biology of trees, tree pruning, the management of the soil, as well as pest control. The certification ensures that the arborist is knowledgeable and has the ability to effectively take charge of the trees.
Consulting Arborists
Consulting arborists offer professional guidance and recommendations to homeowners, businesses and municipalities on how to take care of trees. They can be reached for situations like protecting trees during construction, conflicts resolutions in tree disputes and for help for those with difficult or rare tree diseases. They usually do not carry out any maintenance activities on trees but can give clients direction on how they can manage their trees.
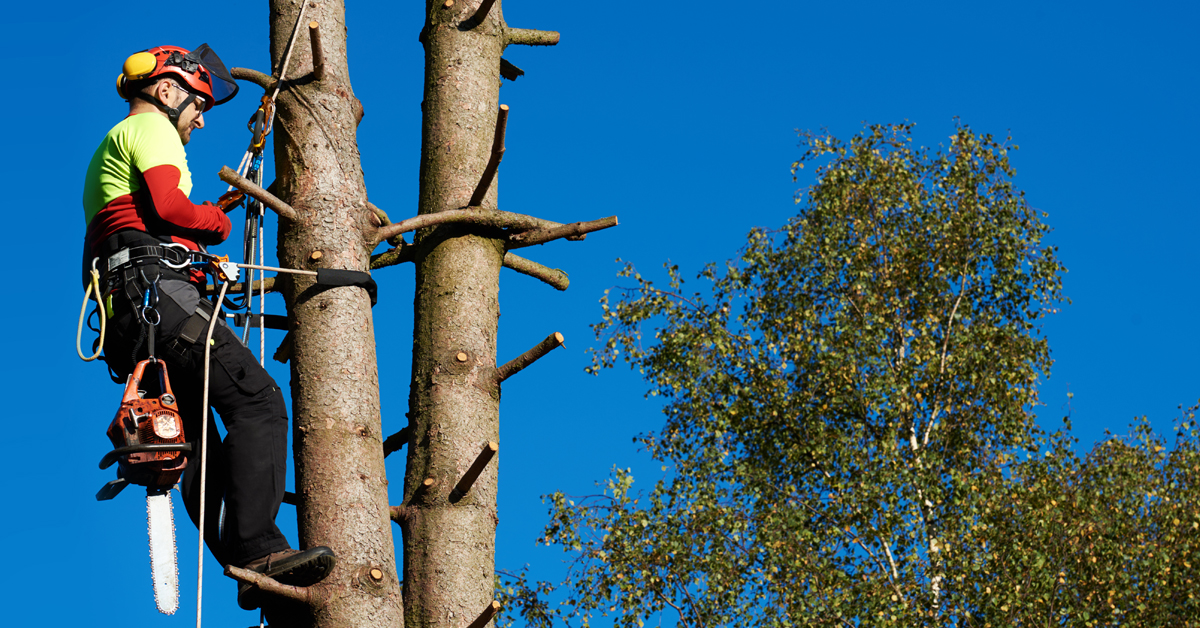
Tree Climbing Arborists
Arborists trained in tree climbing are taught to use harnesses and ropes to climb trees that are too high or otherwise difficult to climb. These arborists typically are people who are responsible for pruning trees, removing them as well as other tasks to maintain on large trees. Arborists who climb receive a strict safety instruction to ensure they can do their tasks without putting other individuals in danger.
5. The Role of an Arborist in Urban Environments
For trees living in urban areas in particular, they face various challenges, like the effects of pollution limits on space, and human activities that may result in the destruction of the roots and branches. Arborists play a crucial role in making sure they thrive for trees in these conditions by making sure that trees are planted, cared for and kept in good condition.
Planting Trees in Cities
Urban areas can be difficult conditions for trees, but arborists are aware of how to choose the right trees for the proper location. If you’re looking for trees that can stand up to drought, water or soil that’s compacted, arborists must ensure that the trees fit to their surroundings. They also ensure proper depth of planting and the security of the roots that is essential to the long-term health of urban trees.
Tree Risk Assessment
In urban areas, trees can cause danger to buildings, roads, and other types of infrastructure. Arborists are specialists in assessing the risk of trees, by assessing the condition of the trees and offering suggestions to reduce the risk. This could include trimming branches, cutting them off or the removal of entire trees that pose a serious risk to the safety of the general population.
6. How Arborists Assess Tree Health
Arborists are specialists in recognizing issues with the health of trees. When they evaluate one particular tree, they look at the many aspects that affect the overall condition and health of the trees. They look at:
- leaves color, and form changes in the hue of a leaf or its shape can suggest a problem. It could indicate a nutritional deficit or illness.
- The trunk and bark Cramps Injuries, evidence that decay is occurring on bark and trunk might be signs of a tree that is weakening.
- Health of roots roots is vital to tree health, and arborists inspect the root system to find signs of rot, disease, or damages resulting from the construction.
Arborists use this knowledge along with their understanding of tree biology to create a treatment plan or suggest steps specific to enhance the overall health and longevity of the tree. The goal is to prevent further harm while ensuring that the tree is strong and healthy.
7. Common Tree Problems and How Arborists Handle Them
Trees face numerous issues throughout their lives, ranging between environmental stresses to diseases and pests. Arborists are experts at identifying the causes and implementing appropriate solutions.
Disease Management
One of the biggest issues for arborists is the problem of tree diseases that are able to rapidly grow and lead to the destruction or even death of trees. The most common tree diseases include:
- Dutch Elm Disease A fungal disease that affects trees of the elm species. It causes wilting, and eventually death. Arborists can prevent this by the detection of disease early and pruning branches affected by the disease and using fungicides.
- Oak Wilt The fungal illness is a concern in oaks, specifically red oaks. The disease is carried by beetles, and has the ability to swiftly destroy trees. Arborists can stop spreading of this disease through trimming off affected branches by avoiding root grafts, and applying specific fungicides.
- Powdery mildew This fungal disease produces a white dusty layer of leaves that slows the growth in the forest. Arborists can control mildew through using fungicides as well as suitable pruning techniques to improve the flow of air.
Arborists are equipped with tools and knowledge to identify the root causes of these issues and efficiently treat trees. They are able to apply the correct treatments or suggest modifications in treatment to ensure the good health of trees.
Pest Control
Pests like aphids caterpillars, and borers are commonly found in the environment and can cause damage to trees. They can damage trees through eating leaves or invading the tree’s trunk or root. Arborists use a variety of strategies to combat insects. For example:
- Pesticides Arborists can apply insecticides to eradicate insects. They ensure that the right chemical is used to control the specific pest, and will minimize the environmental harm.
- Biology Control It is using natural predators for pests, such as ladybugs, which help reduce the number of pests making use of toxic chemicals.
- traps Arborists are able to use traps made from physical materials to capture insects and halt spreading.
In combating insects, arborists prevent the trees from getting damaged, and they also guard other plants in the vicinity.
Soil and Root Problems
The health of trees is directly connected to the soil’s health and the condition that the roots are in. Arborists evaluate the health of the soil and may recommend soil care to boost the amount of nutrients. Most soil problems involve poor drainage, soil that is compacted or a low level of nutrient. Arborists can address these difficulties by improving drainage of their soils or by adding mulch to improve the health of their roots. Root issues, like the impact of construction could be extremely grave. Arborists can employ methods like tree pruning, or even rerouting to limit any harm to the roots that the tree has.
8. The Equipment Arborists Use
Arborists use specialized equipment and tools to complete their tasks in a safe and efficient manner. From trimming trees, climbing up and taking away massive branches, arborists use a variety of tools that allow them to complete their jobs at high elevations and under harsh conditions.
Chainsaws
Chainsaws rank among the important tools used by arborists. They are used to cut branches large enough and to take trees down and for general tree maintenance. Arborists use a variety of chainsaws, depending on the dimension and size of the job. Security is paramount when working with chainsaws. Arborists employ protective equipment to lower the dangers associated with the chainsaw’s usage.
Ropes and Harnesses
If you are at the top tree, arborists depend on ropes and harnesses to aid with climbing the trees secure way. They can climb to the top branches and ensure complete security and control. Arborists utilize techniques for climbing to maneuver through trees and carry out trimming or removing tasks with out damaging the tree or to the arborists.
Wood Chippers
Wood chippers cut the branches or branches to smaller sizes, which makes it easier to eliminate the debris. They are essential for big tree removal tasks and can help to keep the area clean and efficient. Arborists generally employ chippers for small and large tasks depending upon the dimensions of the trees and the number of branches that need to be removed. Polo G
Stump Grinders
If the tree is removed, the arborists typically employ stump grinders to take away the remaining stump. The machines are used to grind the stump down to surface, which can allow for easier replanting or to landscape the space. It’s a vital part in the process of removing trees to make sure that the location is completely cleared.
Pruning Saws and Shears
To cut and trim tasks, arborists use specially designed pruning shears and saws. They are able to cut branches quickly and efficiently, which promotes healthy growth. They can also help arborists get rid of dead wood and damaged trees, while protecting the strength the trees are able to have.
9. Tree Pruning and Trimming Techniques
Pruning and trimming trees isn’t as simple as cutting dead branches. Arborists have specific strategies to keep trees healthy and to avoid damage to trees. Knowing these methods is essential to keep trees safe and healthy.
Proper Timing
When pruning is required it is crucial to check the well-being of the tree. Arborists typically recommend pruning during the dormant stage, which is usually during the early spring months or the winter’s final moment when trees aren’t growing. This helps reduce stress upon the trees, which allows it to heal quicker. Certain trees may require trimming during the growth period according to the particular species and the requirements.
Thinning
Thinning involves the removal of branches in order to allow more light and air to flow into the heart of the trees. This procedure can improve the overall structure of the tree and promotes healthy growth. Through the thinning of the canopy, arborists decrease the likelihood of disease and pest infestations.
Crown Raising
Crown raising is the method of removing lower branches to make room for cars, people or other structures. This technique is usually employed to eliminate trees from urban areas in which branches can hinder walkways, sidewalks or even structures.
Crown Reduction
The process is known as crown reduction. It involves the reducing on the height of trees so that it can maintain its shape and reduce the resistance to wind. This technique is usually employed to decrease the height of trees in mature condition that have become overgrown or have grown beyond their size. Through taking care to decrease the size of their canopy Arborists help keep the trees healthy and less vulnerable to damage by storms.
Deadwood Removal
Deadwood removal is essential in ensuring the trees’ wellbeing as well as their security. Dead or decaying branches could cause danger to the property as well as individuals. Arborists need to remove them fast in order to stop them from falling over and causing damage. Deadwood removal can help the tree channel its energy towards more growth.
10. The Environmental Impact of Arborists
Arborists aren’t only responsible for the care and maintenance of trees as individuals but also play an important role in the protection of our natural environment. Their work directly impacts the well-being of communities, ecosystems, as well as the whole world.
Enhancing Urban Green Spaces
Arborists can improve the general well-being of urban environments by maintaining and planting trees throughout cities and towns. The trees in cities help reduce the harmful effects of pollution as well as provide shade, reduce the price of energy and enhance the quality of the air. Arborists make sure that the trees in urban areas are maintained and are able to continue to bring these vital advantages.
Carbon Sequestration
Trees play a significant role in reducing carbon dioxide levels in our atmosphere. By photosynthesis, trees absorb CO2 and store carbon within their biomass. Arborists can aid in maintaining and enhance processes of sequestration by ensuring healthy trees, and also planting new trees to expand the area of forest.
Supporting Biodiversity
Healthy trees can be a fantastic habitat for wildlife and promote biodiversity in both natural as well as urban settings. Arborists are responsible for ensuring the health of ecosystems by ensuring that the trees are free from disease insects, pests, and environmental stresses. This creates healthy habitats for a variety of species of plants and animals.
11. Becoming an Arborist: Training and Qualifications
An arborist’s job requires formal education and hands-on, and a continuous dedication to learning. Arborists must be educated in the science of tree biology and soil science as well in pest control and techniques to take care of trees. They must also be skilled with the various equipment and tools that go to their work.
Education and Certification
A formal education in horticulture, or the area of arboriculture isn’t necessary in all instances, certain arborists choose to pursue an education in these fields. Alongside their academic training, Arborists who want to pursue becoming arborists typically complete apprenticeships or training on the job to get practical experience within the industry. The accreditation of an organization like The International Society of Arboriculture (ISA) is a crucial step for those looking to grow in their field.
Continuing Education
Tree care is a continuously evolving field, and arborists need to keep up-to-date on the latest techniques, tools practices, as well as regulations. Arborists often participate in conferences and workshops and also attend training courses to stay up-to-date in the current trends in the field. Constant education makes sure that arborists are equipped with the most recent information available to provide the most effective tree maintenance.
12. Why You Should Hire an Arborist
Employing an arborist will assure that your tree is in the best hands. If you need help with the pruning process, disease control or just to ensure that your trees are healthy, An arborist has the expertise and tools to finish the job efficiently and in a safe method.
Expertise in Tree Care
They are trained to be aware of the particular requirements of every kind of tree. They are able to evaluate the condition of the trees that are in your yard, detect potential issues, and suggest solutions tailored to your specific situation.
Safety Considerations
Tree care can be a dangerous job, particularly when you are at a height or when using massive branches that weigh a great deal. Arborists are trained to perform their work in a safe method using the correct equipment and methods, thereby lessening the possibility of injuries.
Long-Term Tree Health
An experienced arborist will ensure that your trees are in good shape for years to come. An effective tree care program can extend the life your trees enjoy as well as enhance their appearance and improve the overall environment that surrounds your property or business.
13. Tips for Hiring the Right Arborist for Your Trees
When deciding on an arborist to work with, it is crucial to select an arborist who has the appropriate qualifications and experience. Here are some tips to select the best arborist to meet your tree care needs:
- Check the authenticity of credentials Verify to determine whether the arborist has been accredited by an established association such as that of the International Society of Arboriculture (ISA).
- References to request Arborists with a good reputation can provide references from clients who have been with them before.
- Request Multiple Quotes Do not take the initial quote. Request quotes from multiple arborists to ensure that you’re getting a reasonable price.
14. Arborists in Disaster Recovery and Storm Damage
After a storm trees are at risk. Arborists are vital to deal with the damage caused by storms, whether it’s cutting down fallen trees, trimming the branches that are damaged, or even checking the condition your trees are. They’re fast and efficient to stop any more damage and remove debris to ensure that you’re safe.
15. The Future of Arboriculture
As the world struggles by environmental challenges like rising temperatures, the work of arborists will grow in importance. From urban areas being reforested as well as fighting the impact of pests and diseases, arborists play a vital part in preserving and growing the number of trees in the world.
Conclusion
Arborists aren’t just tree-care specialists. They are experts with a high level of expertise who protect and enhance the natural landscape and make sure that trees thrive in a world that is constantly changing. No matter whether it’s taking care of the health of a single tree or overseeing the whole urban forest, arborists are at the top of the tree care industry providing a crucial service to the local community as well as the natural ecosystem.
Blog
Dana White Brother: Everything You Need to Know

Dana White, the president of the Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC), is a globally recognized figure in the world of mixed martial arts (MMA). His leadership has transformed the UFC into a multi-billion-dollar enterprise, making him one of the most influential people in combat sports. However, when people search for ” brother,” they often wonder if he has a sibling who shares his success or has contributed to his journey.
In this article, we will explore family background, his relationship with his siblings, and any details available about his brother. We will also discuss his personal life, career, and how his family influenced his path to success.
Who is Dana White?
Early Life and Background
Dana Frederick White Jr. was born on July 28, 1969, in Manchester, Connecticut, USA. He grew up in a middle-class family and was raised primarily by his mother, June White. His father, Sr., was not very involved in his life. White spent a large part of his childhood moving between Las Vegas and New England.
During his teenage years, White developed a passion for boxing and later transitioned into managing fighters. His deep involvement in combat sports eventually led him to acquire the UFC in 2001, alongside Lorenzo and Frank Fertitta. Since then, he has played a crucial role in expanding the UFC brand globally.
Rise to Fame in the UFC
Dana White’s aggressive marketing strategies and business acumen turned the UFC into the world’s leading MMA promotion. Under his leadership, the UFC secured multi-million-dollar broadcasting deals and grew its fighter roster to include some of the biggest names in combat sports. Today, is synonymous with MMA, often making headlines for his outspoken personality and bold decisions.
Does Dana White Have a Brother?
One of the most frequently asked questions about is whether he has a brother. While is a very public figure, he has kept much of his personal family life private. There are no widely known records of a brother who is as famous or involved in his business endeavors.
Family Relationships and Sibling Speculation
Dana White’s immediate family mainly includes his mother, June White, and his sister, Kelly White. There is little to no publicly available information about him having a brother. Some sources suggest he may have distant relatives or step-siblings, but Dana himself has never spoken publicly about having a brother in a way that would indicate a close relationship.
In contrast, Dana has frequently mentioned his sister Kelly, who has been more vocal about their upbringing. In her book King of MMA: An Unauthorized Biography,” their mother, June White, shared stories about their childhood, but she did not discuss any brother figure.
Dana White’s Relationship with His Family
Dana White has a complicated relationship with his family, particularly with his mother. In interviews, he has distanced himself from some of his relatives. His mother’s book, published in 2011, portrayed Dana as someone who changed significantly after gaining wealth and power. She criticized his lifestyle and decisions, which caused further tension between them.
However, despite his strained relationship with his mother, Dana has always focused on building a strong support system around his immediate family, including his wife, Anne White, and their three children.
What About Other Relatives?
Although there is no confirmed record of a biological brother, some fans have speculated about whether Dana has close cousins or step-siblings who could be considered “brothers” in a figurative sense. However, Dana himself has not publicly acknowledged any such relationships.
Why Do People Search for Dana White’s Brother?
There could be several reasons why people are curious about Dana White’s brother:
-
Curiosity About His Family Background – As one of the most powerful men in combat sports, many fans want to know more about his personal life.
-
Speculation About a Hidden Family Member – Some celebrities have long-lost relatives who later gain public attention. This has led people to wonder if Dana has a sibling who might eventually become known.
-
Mistaken Identity – There have been rumors and incorrect reports about individuals being related to , leading to confusion.
Dana White’s Legacy and Influence in MMA
Even without a known brother, legacy is firmly established through his work in MMA. His impact on the sport is unparalleled, and he has built an empire through hard work, business intelligence, and a deep understanding of combat sports.
Key Achievements of Dana White in the UFC
-
Transformed the UFC from a struggling business into a global sports powerhouse.
-
Negotiated billion-dollar deals, including a partnership with ESPN.
-
Expanded MMA globally, introducing the sport to new markets like China, Russia, and the Middle East.
-
Helped build UFC stars like Conor McGregor, Ronda Rousey, and Khabib Nurmagomedov.
Despite controversies, White remains the face of the UFC and continues to grow the sport at an unprecedented rate.
Conclusion
While Dana White has a sister, Kelly White, there is no widely known or confirmed information about him having a brother. His family background remains a topic of interest, but most available records suggest that he does not have a sibling who is involved in his life or business.
Dana White’s success story is a testament to his dedication and business savvy. Whether or not he has a brother, his legacy in the world of MMA is undeniable.
FAQs
1. Does Dana White have a brother?
There are no confirmed reports of having a brother. He has a sister named Kelly White.
2. Who are Dana White’s parents?
Dana White’s parents are June White and Sr. His mother has spoken publicly about their relationship in her book.
3. Is Dana White close to his family?
Dana White has a complicated relationship with some family members, particularly his mother. However, he remains close to his wife, Anne White, and their children.
4. Why do people think Dana White has a brother?
Speculation and misinformation have led people to believe he has a brother, but no confirmed details support this claim.
5. What is Dana White’s net worth?
As of 2024, estimated net worth is around $500 million, primarily due to his ownership stake in the UFC and business deals.
This article clarifies the truth about Dana White’s family and provides an in-depth look at his personal life, career, and influence on MMA. If you’re a UFC fan, stay tuned for more insights into the biggest figures in combat sports!
-

 Tech6 months ago
Tech6 months agoFintechZoom.com – Your Ultimate Guide to Financial News and Insights
-

 Celebrity5 months ago
Celebrity5 months agoWhat Disease Does Michael Keaton Have?
-

 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months agoKittl Design: A Simple Guide to Boosting Your Creative Projects
-
 Tech6 months ago
Tech6 months agoHow to Track a Phone Number on Google Maps
-

 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months agoCute Canva Fonts: A Guide to Adding Charm to Your Designs
-

 Blog5 months ago
Blog5 months agoTimberwolves vs Phoenix Suns Match Player Stats
-
 Entertainment6 months ago
Entertainment6 months agoFlixHQ – Top 10 FlixHQ Alternatives to Watch HD Movies and TV Shows in 2025
-

 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months agoCute Fonts on Canva: A Guide to Adorable Typography for Your Designs
